Throughout this document, we will show you how the features of Lumu can provide you with unprecedented visibility into the adversaries hiding in your network. You will also be able to see how easy it is to incorporate Continuous Compromise Assessment™ into your security operation with Lumu, as well as its versatility.
Network metadata collection is a crucial part of Lumu’s Continuous Compromise Assessment. Lumu can be integrated with your infrastructure using different sources of metadata, including DNS queries and packets, Netflow, Firewall and Proxy logs, in addition to Email Intelligence. Lumu collects network metadata from your on-premise infrastructure, cloud environments, and extended perimeters, including roaming devices.
This model allows any type of network to feed metadata to Lumu and ensures 360-degree detailed visibility that continuously assesses and highlights network threats over all the IT assets in the organization. The following diagram represents some collectors available at Lumu for effective metadata collection for compromise detection.
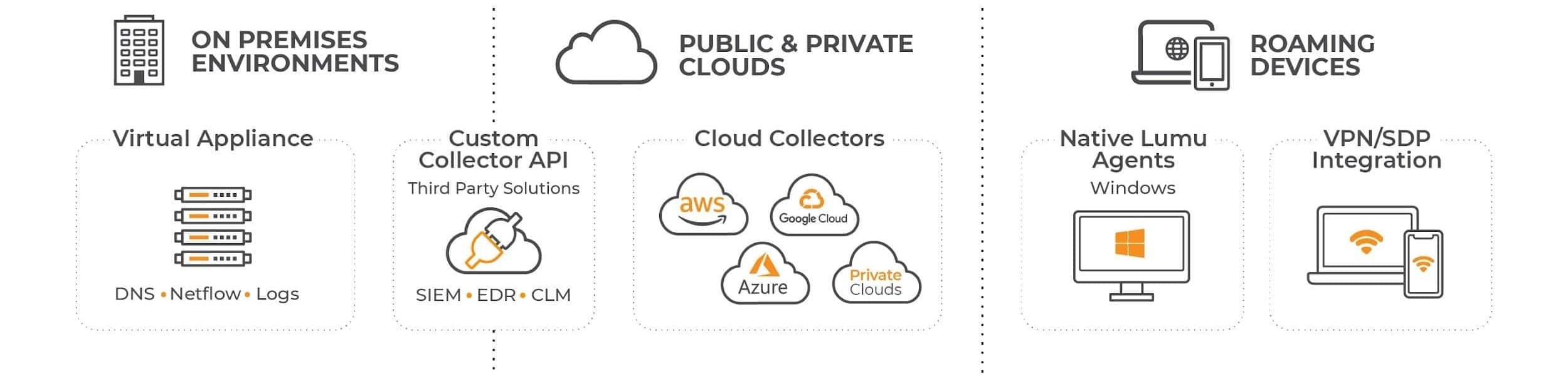 Lumu metadata collectors
Lumu metadata collectors
We know that each infrastructure is unique. We are always looking for new ways to make the metadata collection process as quick and straightforward as possible for your unique reality. Take a look at the different collectors available at Lumu:
| Collector
|
Description
|
| Lumu Virtual Appliances |
The Lumu Virtual Appliance (VA) is a pre-configured lightweight virtual machine solution that collects network metadata of your entire enterprise and forwards it to the Lumu cloud with the lowest impact on the network operation. Lumu VA can be deployed on-premise or as cloud collectors to provide you with detailed malicious activity in your network in real-time.
|
| Gateways |
Associate part of the traffic originating from your organization using Lumu IP addresses as DNS resolvers and illuminate threats, attacks, and adversaries coming from your network.
|
| Agents |
Lumu Agent is an endpoint software program provided by Lumu that is installed on a user's machine and runs silently while continuously collecting network metadata to be analyzed by Lumu for measuring compromise in real-time. This enables the monitoring of remote devices no matter where they are.
|
| Custom Collectors |
Allows sending network metadata captured from third-party platforms/services/appliances, on-premise or cloud, to Lumu via API for frictionless metadata collection and faster compromise assessment .
|

Please note that not all of these metadata sources or collectors are required for having a successful Lumu implementation, only the ones that work best for a specific network. Also, note that some features, such as end-point level visibility and Netflow collection, are only available for Lumu paid subscriptions. For more details, consult
Lumu Offerings.
The following scenarios illustrate how to deploy Lumu for each type of metadata, considering the network infrastructure and architecture:
Firewall and Proxy Collection
Firewall and proxy logs give maximum visibility into compromises in your network. This option is available for accommodating networks where DNS configuration is not possible. This is the recommended metadata collection strategy if available in your organization, as when you collect Firewall and Proxy metadata, DNS resolution metadata becomes superfluous.
In this scenario, companies can monitor IP traffic, while the Lumu Virtual Appliance or Custom Collector API acts as a firewall or proxy log collector.
In networks where a proxy or a firewall are available, they can be configured to forward logs to Lumu’s VA for processing all IP addresses contacted by the monitored assets. If TLS inspection is enabled on the firewall, you will also have visibility into domains and URLs visited using HTTPS.
This approach ensures compromise visibility without requiring major changes, as almost every firewall brand can forward logs externally without impacting their operation. It is also the recommended option for companies that want to minimize any risk to operation, as an issue in the Virtual Appliances will not affect the functionality of the network.
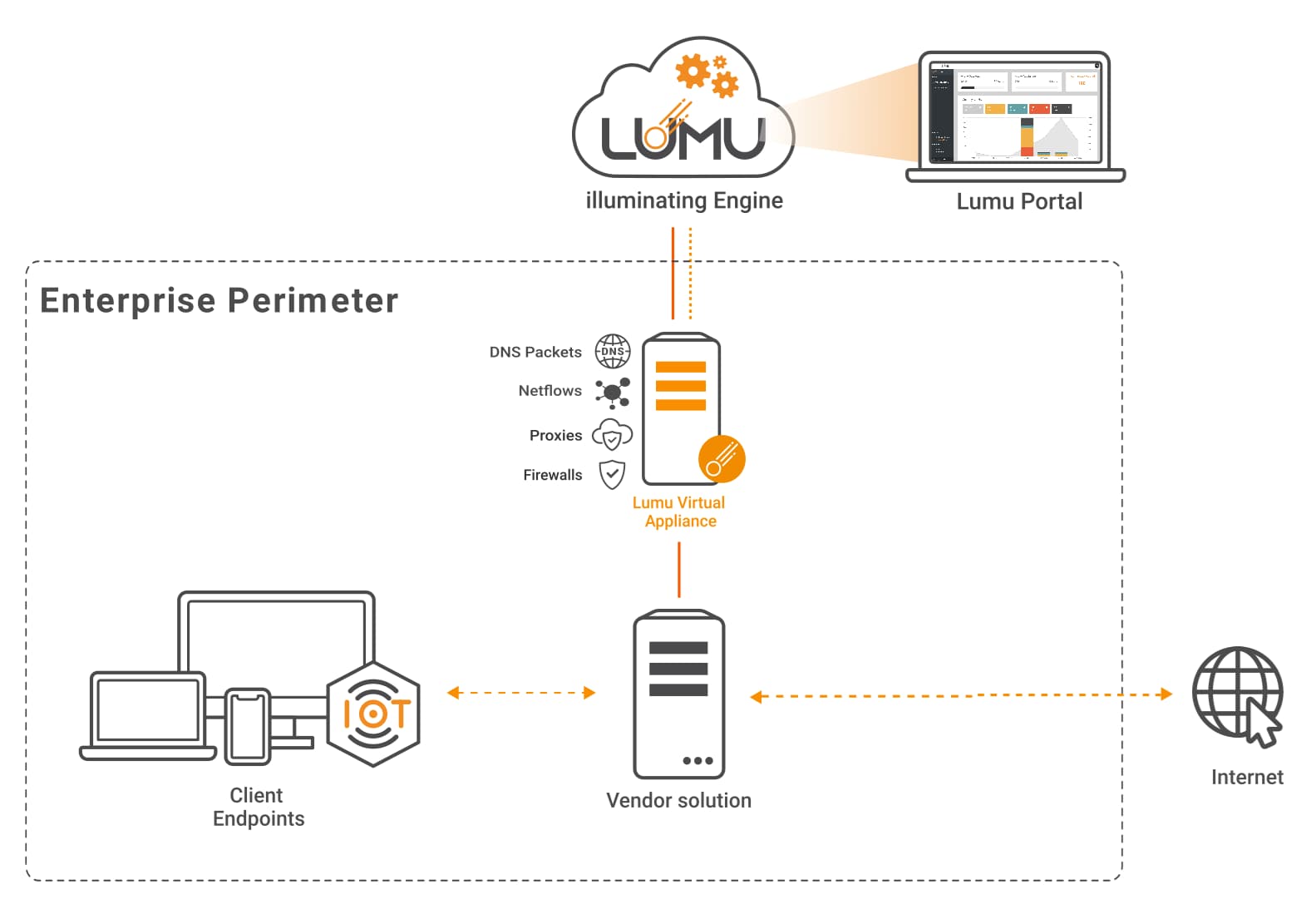 Network diagram with Lumu VA for metadata collection
Network diagram with Lumu VA for metadata collection
A similar approach can be taken to integrate metadata collected by Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) technologies, as shown in the following diagram:
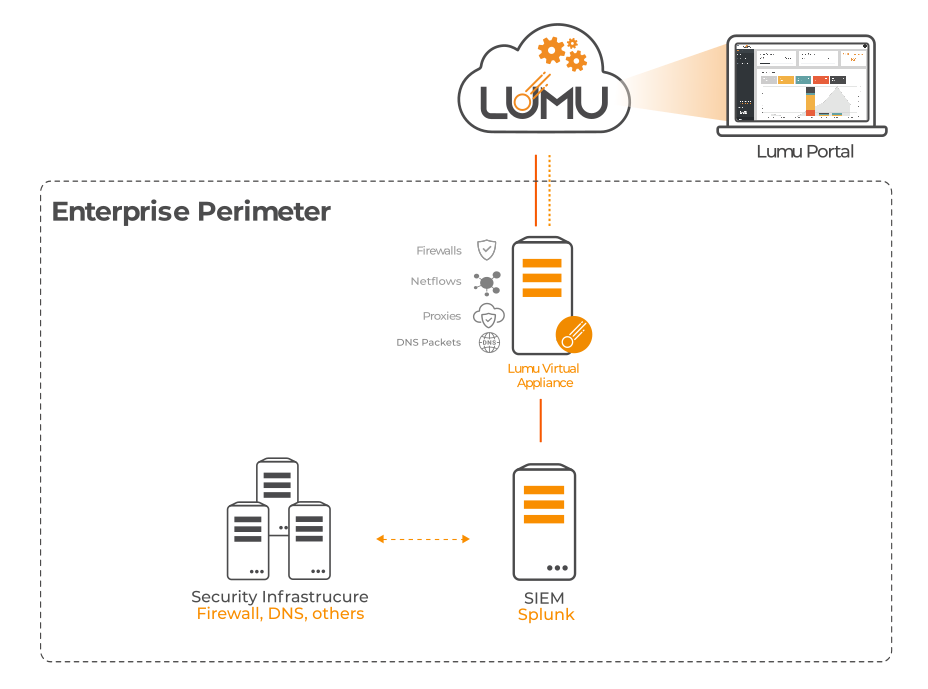 Network diagram with Splunk integrated
Network diagram with Splunk integrated
Related documentation:
We created guides to illustrate the configuration with some third-party solutions. The process would be very similar for any other vendors:
- Collect Metadata with Lumu VA
- Collect Metadata with Lumu VA and Splunk

Lumu offers the option for ingesting firewall logs from third-party solutions, such as networking monitoring tools, through an API-based collector. See the topic “API-based Collection” below for more details.
DNS Collection
DNS queries and packets provide context into the organization’s devices’ connection attempts with adversarial infrastructure.
Take advantage of Lumu Public Gateways to associate part of the traffic originating from your organization to Lumu for illuminating threats, attacks, and adversaries coming from your network. You also have the option to configure third-party solutions to forward DNS queries to Lumu. This option is recommended when a centralized control of the DNS servers used by the assets is available. Public Gateways are the fastest and easiest way to deploy Lumu in your organization, but keep in mind that this collection method does not provide visibility into the assets making queries.

Gateways can be configured to represent departments, offices, or geographic regions, whichever makes the most sense for your unique organizational structure.
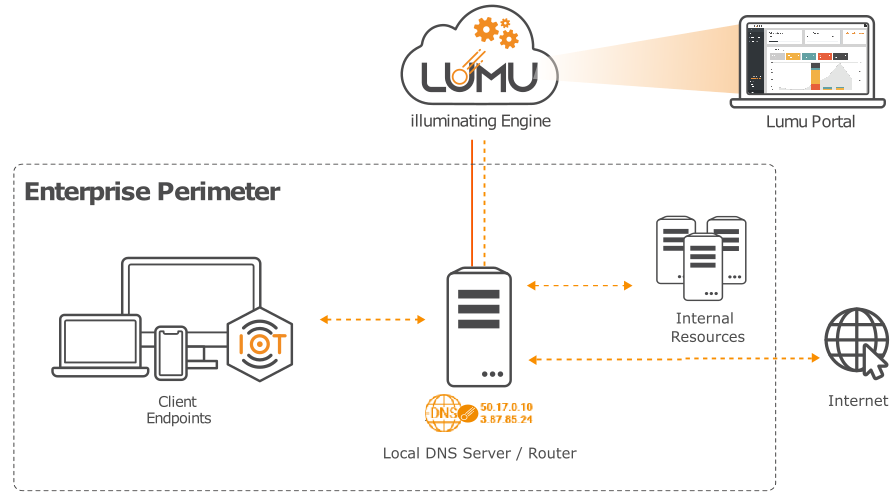 Example of an enterprise perimeter pointing DNS to Lumu Gateways
Example of an enterprise perimeter pointing DNS to Lumu Gateways
Related documentation:
- Using Lumu Public Gateways as Primary DNS Resolvers
- Collect DNS queries with Lumu Gateways and Infoblox
Collect DNS Packets Metadata from a Domain Controller
In the scenario, of small offices where the network has a domain controller acting as a DNS server, those assets can be monitored by a Lumu VA that can receive and process DNS metadata from multiple domain controllers. This approach does not require modifying the network configuration.
In this scenario, Lumu offers the possibility to install a lightweight application (Packetbeat) in the domain controller, which would be in charge of sending the DNS metadata to the Lumu Virtual Appliance, which can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud.
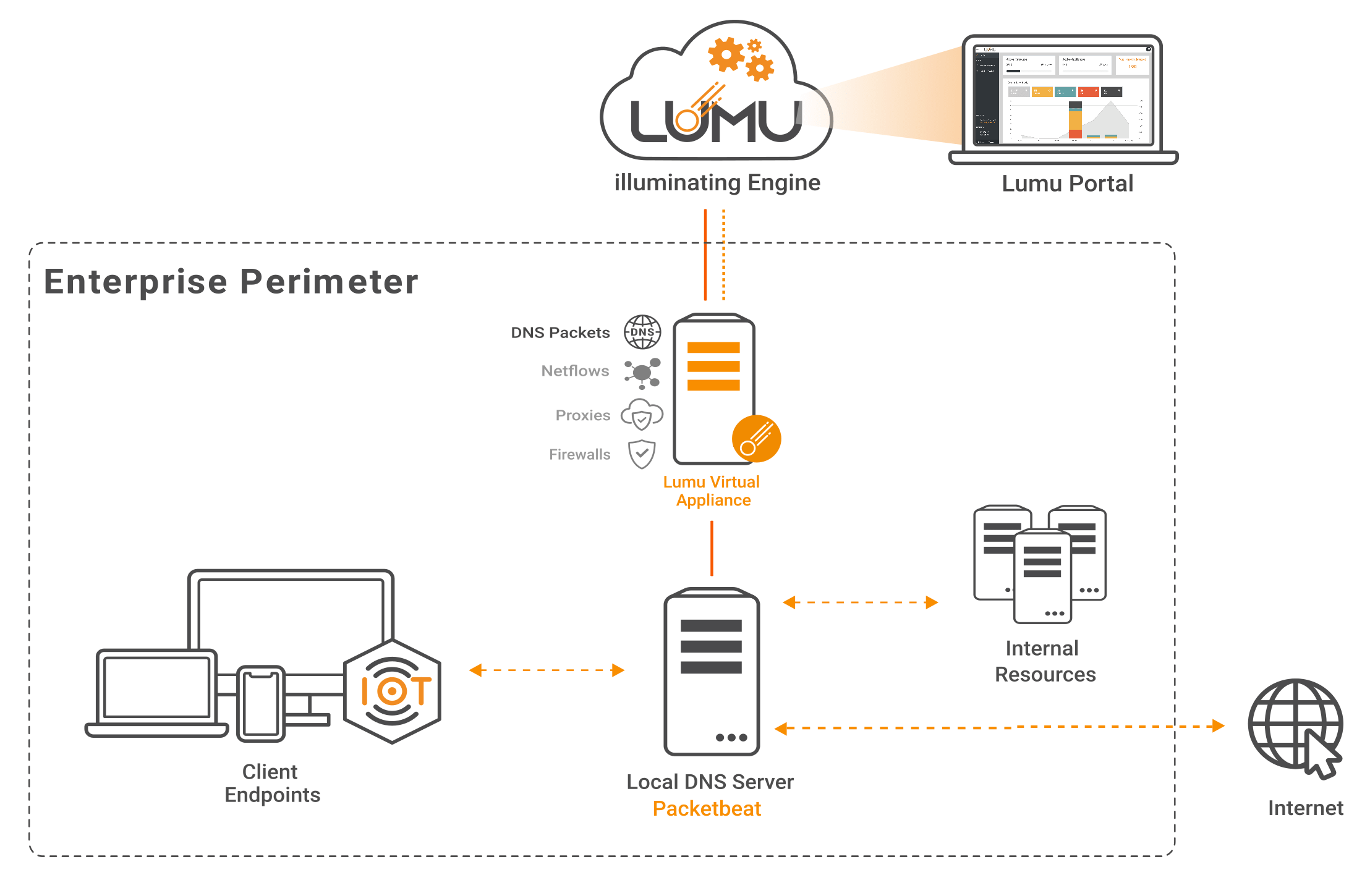 Metadata collection diagram for Lumu VA and Packetbeat
Metadata collection diagram for Lumu VA and Packetbeat
Related documentation:
- Collect DNS packets with Lumu VA and Packetbeat
The Lumu VA comes equipped with all the resources needed to work as a DNS resolver. This scenario is ideal for environments without a domain controller. This would require the DHCP to use Lumu's VA as the main DNS resolver for the network or its assets.
As you can see in the following graphic, when using the Lumu VA’s built-in DNS resolvers, all DNS resolution metadata is sent to the Lumu Cloud for Continuous Compromise Assessment.
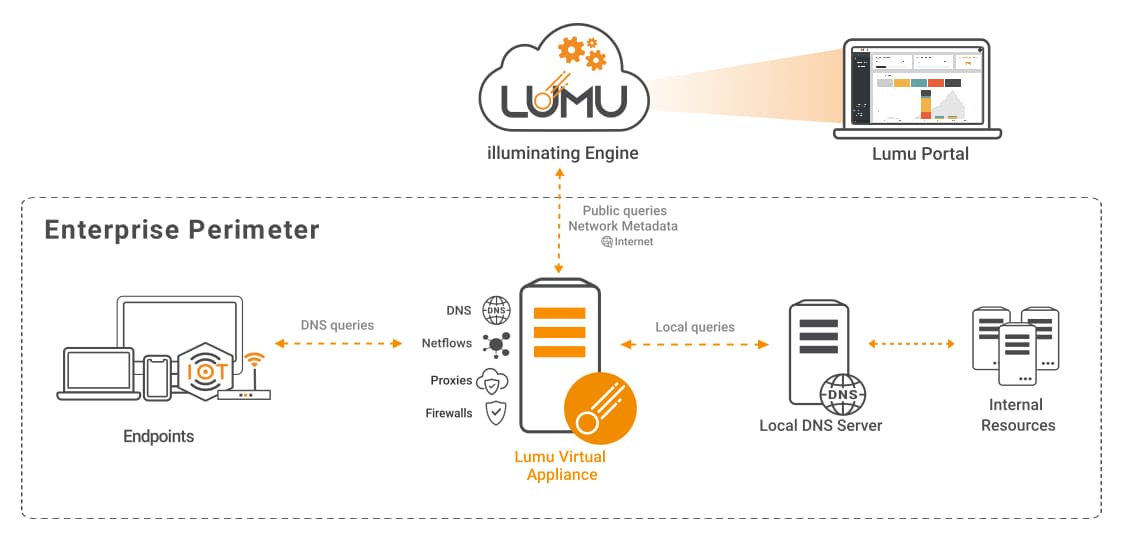 Infrastructure with Lumu VA as DNS Resolver
Infrastructure with Lumu VA as DNS Resolver
Related documentation:
- Set Lumu as primary network DNS Resolver on Virtual Appliances
You also have the option to deploy the Lumu VA as a collector of DNS queries. This case applies when you are not using the virtual appliance’s built-in DNS resolver but still using the VA for collecting DNS metadata.
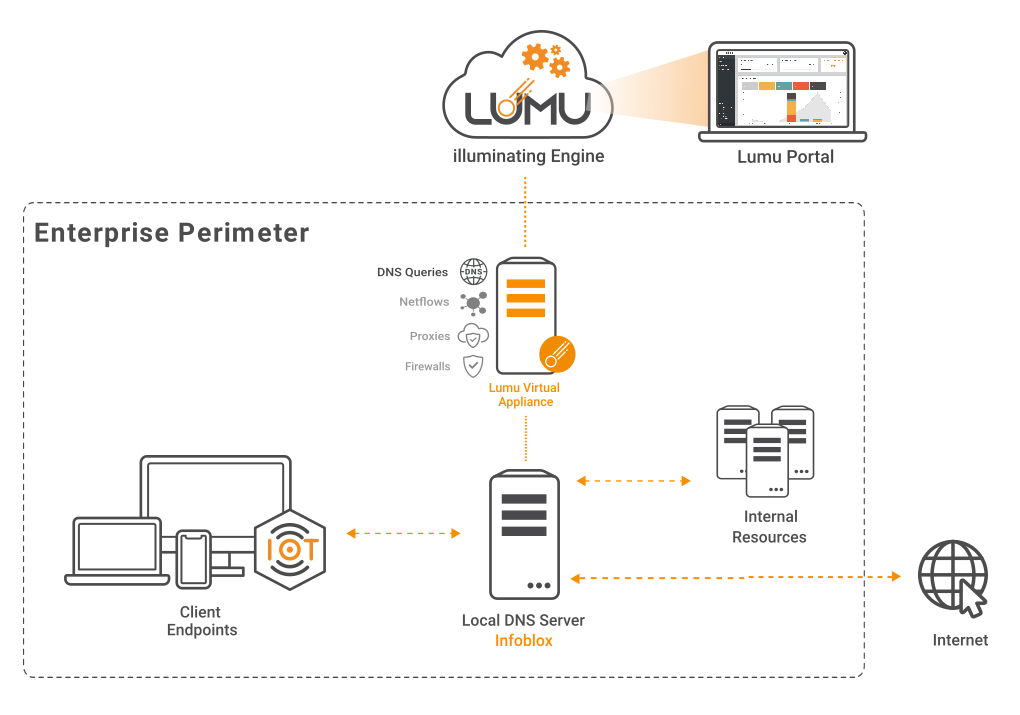 Network diagram with Lumu VA Collector for Infoblox
Network diagram with Lumu VA Collector for Infoblox
Related documentation:
- Collect DNS queries with Lumu VA and Infoblox
Netflow Collection
An on-premise Lumu VA can act as a netflow collector, provided the availability of network devices capable of generating netflows or IPFIX. The preferred arrangement consists in setting up the core switches to send netflow logs for maximum visibility. For devices not equipped with netflow capabilities, using a Network TAP device or an auxiliary device capable of synthesizing netflow from a mirror interface may be an option.
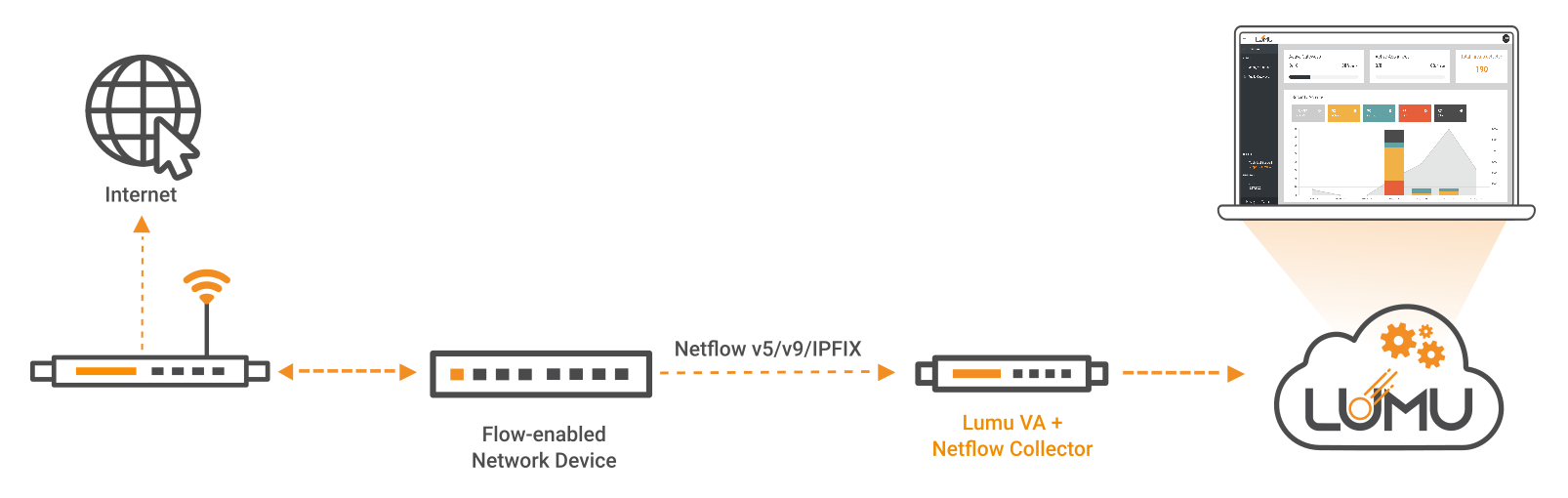 Network flow collection with flow-enabled network devices
Network flow collection with flow-enabled network devices
Related documentation:
- Configure Netflow/IPFIX Collector on Lumu Virtual Appliance
Remote Assets
In cases where IT assets don’t use the company’s network to navigate the internet, or none of the previous configurations can be done, companies can still have compromise visibility by deploying Lumu Agents to monitor the connections from those devices regardless of the network they use.

The Lumu Agent is an endpoint software program provided by Lumu, which is installed on a user's machine and runs silently while continuously collecting network metadata to be analyzed by Lumu for measuring compromise in real-time.
The agent captures the information from the device and sends it to Lumu’s cloud directly. A Lumu VA is not required, nor is any additional configuration. This scenario can be helpful in cases where companies cannot deploy a virtual appliance. Agents are usually massively deployed with ease in such environments.
For organizations with a remote workforce, besides Installed Agents, Lumu also offers the option to implement the Continuous Compromise Assessment concept using VPN (Virtual Private Network) or SDP (Software Defined Perimeter) technologies.
 Roaming Infrastructure with Lumu Agent or VPN/SDP
Roaming Infrastructure with Lumu Agent or VPN/SDP
Related documentation:
- Lumu Agent
- VPN/SDP Configurations
Email Intelligence
Email is an attacker’s preferred method to deliver exploits. Lumu can analyze an organization's emails to provide insights into the type of attacks an organization is facing. More importantly, Lumu can determine if end-users are accessing such attacks and if the organization is at a high risk of compromise.

The Lumu Email Intelligence feature ingests spam metadata and runs advanced correlations between emails in your inbox, known IoCs, and network traffic to support the Continuous Compromise Assessment of your organization.
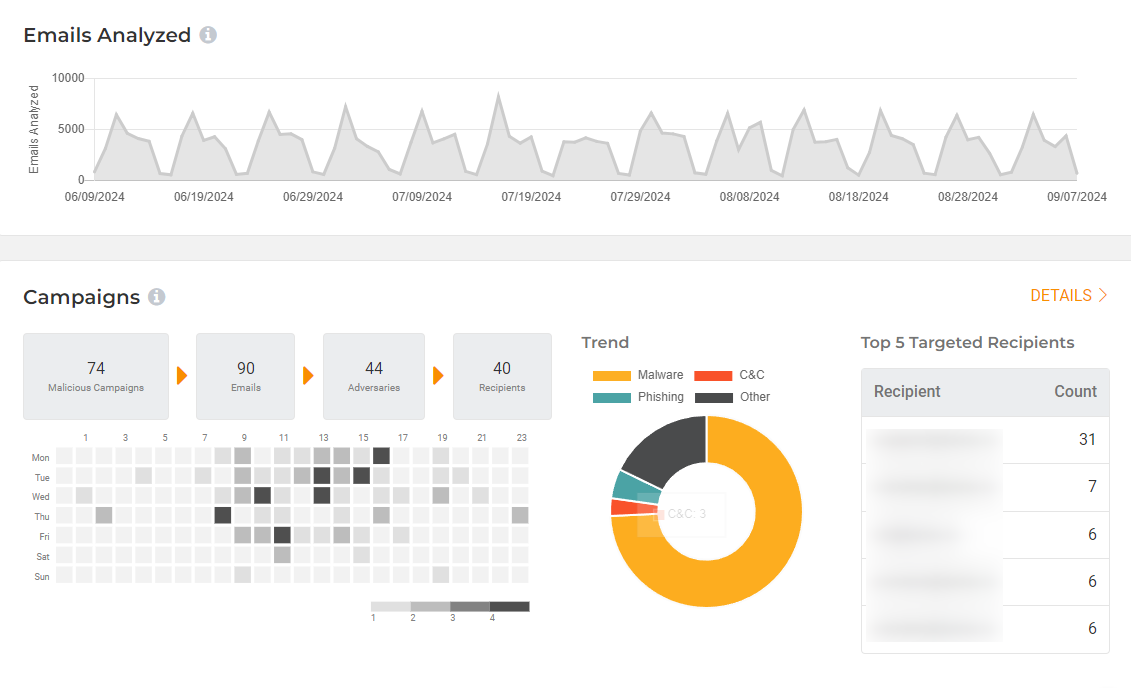 Lumu Email Intelligence Dashboard
Lumu Email Intelligence Dashboard Related documentation:
- Lumu Email Intelligence
API-based Collection
Some enterprises are already using defense solutions such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or network monitoring tools as part of their pipelines to centralize their logs. In this scenario, Lumu gives the option to deploy the Custom Collector API to ingest your metadata via API. This allows third-party network solutions—on-premise or cloud-based—to communicate directly with Lumu’s cloud to feed metadata.

Please keep in mind that Netflow metadata collection requires a Lumu VA.
 Infrastructure with Lumu Collector API
Infrastructure with Lumu Collector API
Related documentation:
- Custom Collectors
Integrations for Automated Response
Lumu Defender API also offers customers the ability to feed Lumu's confirmed compromise instances into your existing cybersecurity stack for an automated response to cyber threats, as illustrated in the figure below.
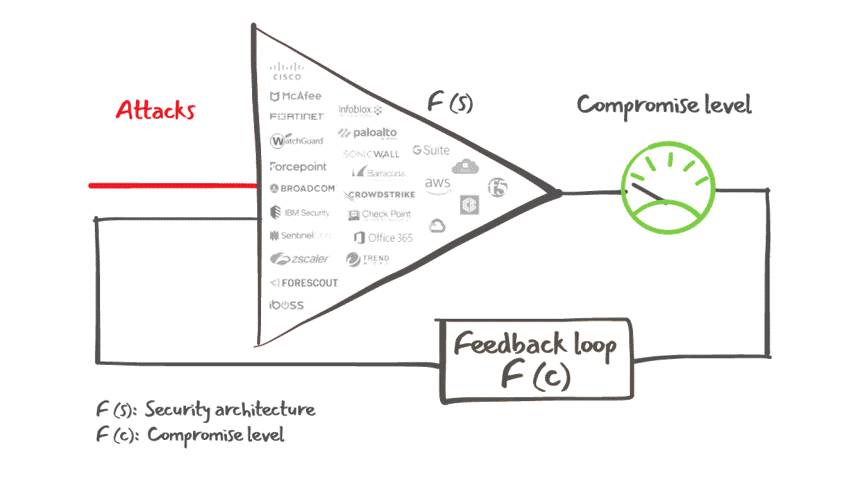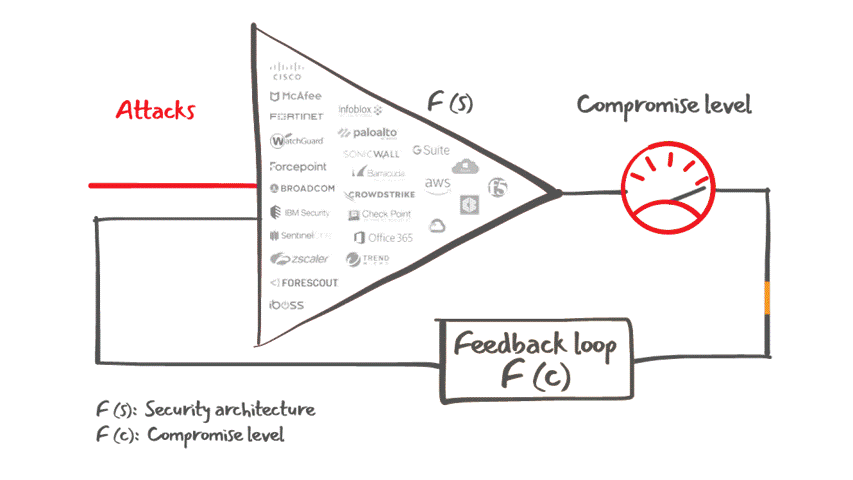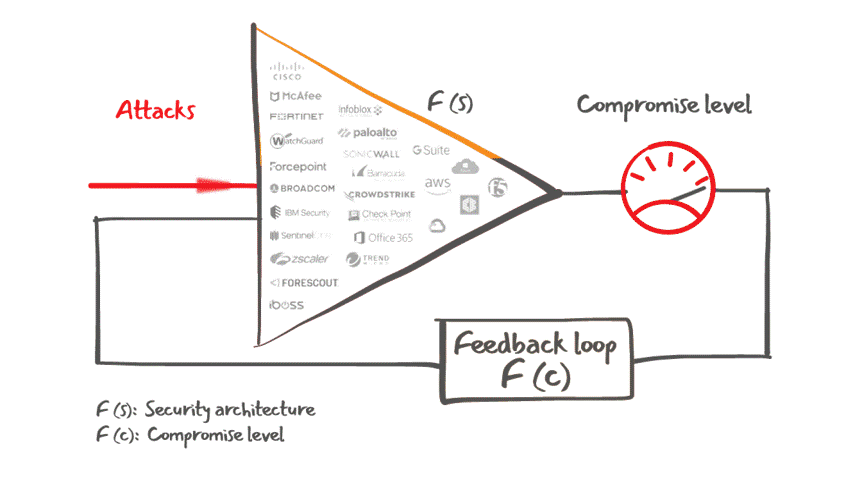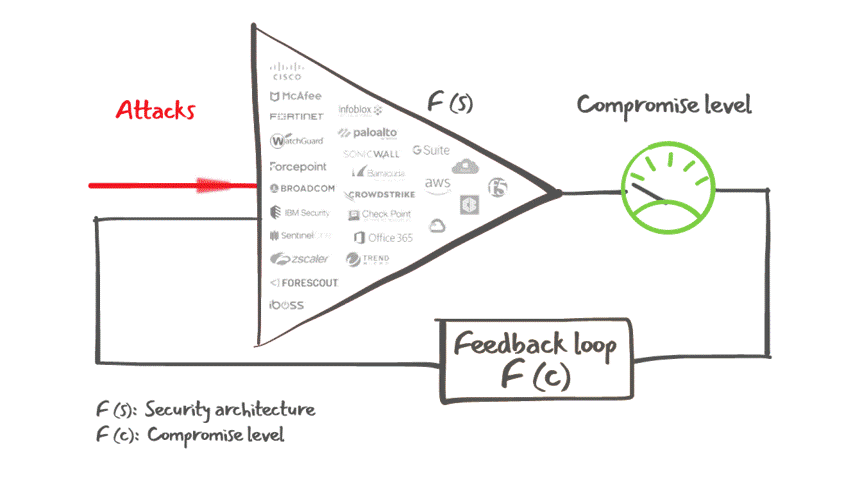 Lumu Defender and its integrations capabilities
Lumu Defender and its integrations capabilities
Related documentation:
- Integrations






